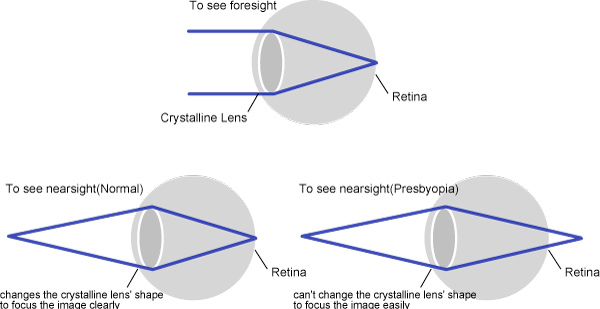
Presbyopia is a vision condition in which the crystalline lens of your eye loses its flexibility, which makes it difficult for you to focus on close objects.
Some signs of presbyopia include the tendency to hold reading materials at arm's length, blurred vision at normal reading distance and eye fatigue along with headaches when doing close work. A comprehensive optometric examination will include testing for presbyopia.
Treatments
Corrective lenses
If you had good, uncorrected vision before developing presbyopia, you may be able to use nonprescription over-the-counter reading glasses
Refractive surgery
Refractive surgery changes the shape of your cornea. For presbyopia, this treatment — equivalent to wearing monovision contact lenses — may be used to improve close-up vision in your nondominant eye.
Lens implants
Another procedure used by some ophthalmologists involves removal of your clear natural lens and replacement with a synthetic lens inside your eye (intraocular lens implant). Some newer lens implants are designed to allow your eye to see things both near and at a distance.
Some signs of presbyopia include the tendency to hold reading materials at arm's length, blurred vision at normal reading distance and eye fatigue along with headaches when doing close work. A comprehensive optometric examination will include testing for presbyopia.

Treatments
Corrective lenses
If you had good, uncorrected vision before developing presbyopia, you may be able to use nonprescription over-the-counter reading glasses
Refractive surgery
Refractive surgery changes the shape of your cornea. For presbyopia, this treatment — equivalent to wearing monovision contact lenses — may be used to improve close-up vision in your nondominant eye.
Lens implants
Another procedure used by some ophthalmologists involves removal of your clear natural lens and replacement with a synthetic lens inside your eye (intraocular lens implant). Some newer lens implants are designed to allow your eye to see things both near and at a distance.



